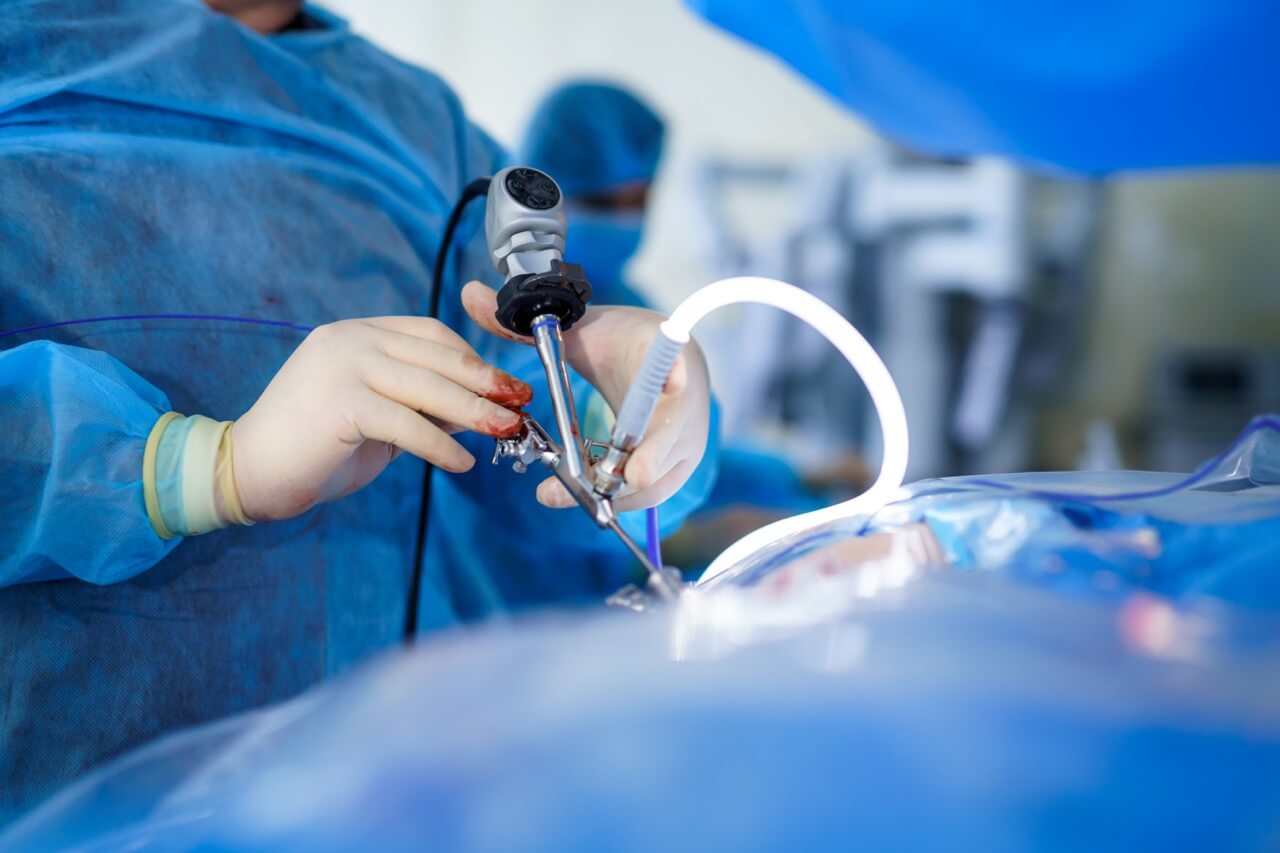
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique performed by inserting a small camera and instruments into the abdominal cavity. In this method, a camera and surgical instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity through small incisions made in the abdominal wall. This allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the abdomen and perform surgical interventions.
Advantages of Laparoscopy
The advantages of laparoscopy emerge in various areas compared to traditional surgical methods. There are many benefits to choosing this minimally invasive surgical technique.
– Less pain: Laparoscopy is associated with less pain. This allows patients to have a more comfortable recovery process after surgery.
– Smaller incisions: Instead of large incisions made in traditional surgical methods, laparoscopy requires only small incisions. This results in better aesthetic outcomes.
– Less bleeding: The special instruments and techniques used during laparoscopy minimize the risk of bleeding. This leads to less postoperative bleeding for patients.
– Faster recovery: Laparoscopy minimizes trauma to the body, allowing for a faster recovery process. Patients can typically return to normal activities sooner.
The Role of Laparoscopy in Gynecology and Infertility
Laparoscopy provides significant advantages compared to open surgeries in many gynecological procedures, including shorter operation times, smaller incisions, reduced hospital stay, decreased risk of adhesion formation, quicker recovery, and lower cost.
Laparoscopy can be performed for diagnostic or operative purposes and is commonly used in the following conditions:
– Evaluation and treatment of infertility
– Evaluation and treatment of ovarian cysts
– Diagnosis and treatment of gynecological cancers
– Treatment of fibroids
– Uterine surgeries
– Management of ectopic pregnancy
– Tubal ligation
– Treatment of hydrosalpinx
– Surgery for endometriosis
– Treatment of chronic pelvic pain
– Surgery for pelvic floor defects and urinary incontinence
In female infertility, pathology in the fallopian tubes is a significant factor, and if any blockage is observed in hysterosalpingography (HSG), laparoscopy can be performed. In the presence of hydrosalpinx (fluid accumulation due to blockage in the tubes), embryo implantation rates decrease, pregnancy rates decrease by 50%, and the rates of miscarriage double. The decrease in pregnancy rates parallels the size of the hydrosalpinx, and in these patients, salpingectomy (removal of the diseased tube) or proximal tubal ligation (tying off the tube to disrupt the connection between the uterus and the tube) can be performed with laparoscopy.
Laparoscopic adhesiolysis (opening of adhesions) and fimbrioplasty (tube surgery) are methods that can be used to increase fertility when necessary.
A procedure called laparoscopic ovarian drilling, which we call ovarian drilling, can be attempted in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) before undergoing IVF treatment in terms of reproductive outcomes. However, due to the risk of significant complications such as early menopause and adhesions, it is recommended to be performed only by an experienced endoscopic gynecologist.
Another important disease underlying female infertility is endometriosis. Endometriosis is a disease that affects 10-15% of women of reproductive age and is present in 30-50% of infertile women. In patients with endometriosis without other risk factors, pregnancy rates may increase after laparoscopic surgery. Although previous studies have shown the benefits of laparoscopic surgery in mild and minimal endometriosis, clear evidence has not been established in advanced-stage endometriosis. However, evaluating the surgical intervention plan on a patient-by-patient basis within the framework of infertility can prevent unnecessary interventions. It should be noted, however, that delaying pregnancy after laparoscopic endometriosis surgery is associated with lower pregnancy rates and higher recurrence rates.
Risks of Laparoscopy
Although laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method, it may also carry some risks. These are usually rare occurrences but should still be considered. Laparoscopy can carry risks such as infection, bleeding, and organ injury, albeit rarely. The risk of infection exists during laparoscopy, as in any surgical procedure. However, this risk can be minimized when sterilization and hygiene measures are taken.
Bleeding may occur due to damage to instruments or tissues during laparoscopy. This risk is quite low in procedures performed by expert surgeons, but caution should still be exercised.
Organ injury is an unwanted condition detected during or after laparoscopy, either clinically or through subsequent symptoms. This condition is seen at a very low rate in procedures performed by experienced surgeons. The risk of organ injury is higher in diseases involving intra-abdominal adhesions, such as endometriosis.
To minimize all these risks, a detailed evaluation should be conducted before the laparoscopic procedure, and the operation should be performed by an experienced surgeon. Additionally, it is important to regularly monitor patients during the postoperative period and conduct necessary follow-up examinations.
Complications of Laparoscopy
Deterioration of the patient’s condition or abnormalities in vital signs, which are expected to improve day by day after laparoscopic surgery, may indicate the development of any complications.
Complications of gynecological laparoscopy range from 0.1% to 10%, with major laparoscopic procedures having a higher complication rate compared to minor laparoscopic surgeries.
One-third of complications occur during laparoscopic setup and entry into the abdomen, while one-fourth occur during surgery and may not be apparent at that time. The surgeon’s experience also plays a role in the development of complications. The majority of complications occur during entry into the abdomen or during insufflation of the abdominal cavity with gas. Moreover, patients who have previously undergone intra-abdominal surgery, those with endometriosis, inflammatory tubal disease, or tubo-ovarian abscesses, and those with adhesions are at a higher risk of complications.
Complications of Laparoscopy
Among the complications of laparoscopy, bowel injury, urinary tract injury, and thromboembolic events (blood clotting) may occur. Bowel injury can occur when the instruments inserted into the abdominal cavity during laparoscopy damage the intestines, which may require surgical intervention. Urinary tract injury can occur due to damage to the urinary tract, such as the bladder or ureter, leading to problems such as urinary leakage or disruption of urinary flow.
Thromboembolic events are also among the complications that may occur after laparoscopy. These events occur as a result of the formation of blood clots and obstruction of blood flow, especially during prolonged surgical procedures and periods of immobility. Therefore, patients should be encouraged to move after laparoscopy, and measures should be taken to improve blood circulation.
Recovery Process After Laparoscopy
Patients generally recover faster and experience less pain after laparoscopy. This minimally invasive surgical method has many advantages over open surgery. The recovery process after laparoscopy shortens the time for patients to return to daily activities and reduces the length of hospital stay.
During the recovery process after laparoscopy, patients typically experience minimal pain and usually do not require painkillers. This allows patients to move more comfortably and continue their daily activities.
The recovery process after laparoscopy also provides advantages in terms of wound healing. Because the small incisions used during laparoscopy are smaller and require fewer stitches compared to open surgery, wound healing is faster and less prone to complications.
Additionally, the dietary habits of patients typically return to normal more quickly after laparoscopy. Patients can usually transition to liquid foods earlier and experience less nausea or vomiting after laparoscopy.
Points to Consider During the Recovery Process After Laparoscopy
There are some points that patients need to pay attention to during the recovery process after laparoscopy. You should regularly care for the wound as recommended by your doctor, avoid heavy lifting and move, and pay attention to hygiene rules to prevent infection. Generally, the recovery process after laparoscopy is faster and less painful for patients. However, the recovery process may vary for each patient, so it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and attend regular follow-up appointments.
Follow-up After Laparoscopy
Follow-up of patients after laparoscopy is essential. During this process, patients should be regularly monitored by their doctors and necessary checks should be performed. The follow-up process is important for monitoring the patients’ health and early detection of possible complications.
During the follow-up process, the general health status of patients, wound healing, and pain levels are evaluated. Additionally, complications that may occur after laparoscopy, such as infection or bleeding, are also monitored. Therefore, patients should attend their follow-up appointments regularly and inform their doctors of any problems or complaints.
Follow-up appointments may include blood tests, imaging methods, and physical examinations. Doctors perform these checks to monitor the patients’ recovery process and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Additionally, there are some precautions that patients should take after laparoscopy. These precautions may include wound care, dietary adjustments, and activity regulation. Doctors provide patients with necessary information on these matters and specify the rules to be followed during the follow-up process.
It should be noted that the follow-up process after laparoscopy is extremely important for maintaining patients’ health and preventing potential complications. Therefore, it is crucial for patients to maintain regular communication with their doctors and adhere to follow-up appointments.
Laparoscopy is a closed surgical system performed by inserting a small camera and instruments into the abdominal cavity. Generally, three small incisions (5-10 mm) are made, one at the navel and two in each groin area.
Laparoscopy has advantages such as less pain, smaller incisions, less bleeding, and faster recovery.
Laparoscopy is used in many different surgical procedures such as infertility diagnosis and treatment, hysterectomy, myomectomy, tubal ligation, urinary incontinence surgeries, cervical cancer, and uterine cancer surgeries.
Although rare, complications such as organ injury, bleeding, and thromboembolic events may occur in laparoscopy.
By filling out the form, you can make an appointment with Gynecology and Obstetrics Specialist Prof. Dr. Ebru Çöğendez.

IVF treatment prices usually include factors such as tests, medications, laboratory procedures, doctor examinations, etc. during the treatment process.

IVF treatment is applied to couples who are determined by taking certain factors into consideration.

Factors such as age, health status, choice of treatment center and treatment process can affect success rates.

The stages of IVF treatment usually consist of four main stages. The first stage is the preparation stage.

As with any medical intervention, IVF treatment has potential risks and possible complications.